Electrical Discharge Machining: Working, Principle, Uses with PDF and Case Study
Introduction to Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Electric Discharge Machining (EDM), a fascinating manufacturing process that has revolutionized the way we shape and mold various materials.
Whether you’re a mechanical engineering enthusiast or simply curious about advanced machining techniques, this detailed and well researched blog article brought to you by The Mechanical post will provide you with a detailed understanding of EDM, its principles, applications, and the benefits it offers.
At the end of the article you can find the FREE PDF on Electric Discharge Machining to learn and understand this topic later whenever you like…
What is Electrical Discharge Machining?
So, what exactly is Electrical Discharge Machining? Well, EDM is a non-traditional machining method that utilizes electrical discharges, or sparks, to shape and form workpieces. Unlike conventional cutting tools, EDM does not rely on direct physical contact between the tool and the material. Instead, it employs controlled electrical discharges to erode the material, resulting in intricate and precise shapes.
The EDM is used for machining very hard materials which would not have been possible using traditional machining processes like lathe machine, milling machines, etc. The Electrical Discharge Machining process is also known as spark eroding or spark machining.
This makes EDM an ideal choice for producing molds, dies, and components that require high precision and surface quality.
EDM has gained immense popularity in the manufacturing industry due to its versatility and ability to work with a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, ceramics, and even hardened tool steels. It has found applications in various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical device manufacturing.
One of the key advantages of EDM is its ability to produce intricate and complex shapes that are often challenging or impossible to achieve with traditional machining methods. By using electrical discharges, EDM can precisely remove material from the workpiece, allowing for the creation of intricate geometries, sharp corners, and fine details.
Moreover, EDM is particularly well-suited for machining hard and brittle materials. Since the process doesn’t rely on physical force, it minimizes the risk of material damage or distortion that can occur with traditional cutting methods.
Throughout this article, we will explore deeper into the principles that drive Electrical Discharge Machining, explore its various applications in different industries, and highlight the benefits it provides. We’ll also address common questions and concerns related to EDM, ensuring that you have a well-rounded understanding of this cutting-edge manufacturing technique.
So, let’s embark on this enlightening journey into the world of Electrical Discharge Machining, where sparks create wonders and precision knows no bounds.
Understanding the Principles of Electrical Discharge Machining
EDM is based on the phenomenon of electrical discharge, where sparks are generated between an electrode and the workpiece. The electrode, typically made of copper or graphite, is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, while the workpiece is connected to the negative terminal. A dielectric fluid, such as hydrocarbon-based oil or deionized water, surrounds the machining area.
Now that we have a basic understanding of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), let’s dive deeper into the principles that drive this fascinating process.

At its core, EDM harnesses the power of controlled electrical discharges to shape and erode material. The process relies on the principle of electrical discharge, which occurs when a voltage potential is applied between an electrode (tool) and a workpiece, submerged in a dielectric fluid.
As the voltage is increased, a potential difference is established between the electrode and the workpiece, creating a localized spark discharge. This discharge generates intense heat, melting and vaporizing the material in its path.
Let’s take a closer look at the working principle of EDM. There are different techniques employed in EDM, but two of the most common ones are:
Wire EDM (WEDM) and Sinker EDM (SEDM).
In Wire EDM, a thin, electrically conductive wire is used as the electrode, while in Sinker EDM, a shaped electrode, often made of graphite or copper, is used to erode the material.
In Wire EDM, a thin wire is continuously fed through the workpiece, forming a precise cut along the desired path. This technique is particularly useful for creating intricate shapes and contours. For example, in the aerospace industry, Wire EDM is employed to cut cooling holes in turbine blades or to produce complex airfoil shapes with utmost precision. Almost 0 Tolerance parts can be manufactured using it.
On the other hand, Sinker EDM involves submerging the electrode into the dielectric fluid and positioning it close to the workpiece. Electrical discharges occur between the electrode and the workpiece, eroding the material in a controlled manner.
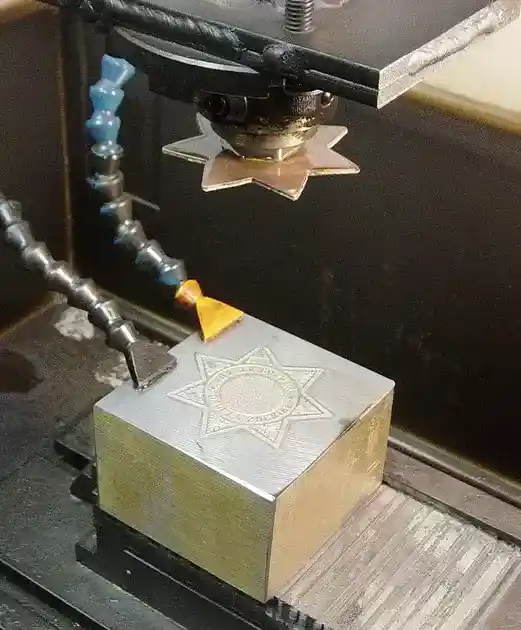

Source: Leonard G. at English Wikipedia., CC SA 1.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Sinker EDM is commonly used in the production of molds, dies, and other components that require intricate details and high surface finishes. For instance, in the automotive industry, Sinker EDM is utilized to manufacture precise injection molds for complex plastic parts.
Another variation of EDM is EDM Drilling, also known as Hole Popper. This technique employs a rotating electrode to drill small holes in the workpiece. EDM drilling finds application in industries such as aerospace and medical device manufacturing, where precise, high-quality holes are required in materials like titanium and stainless steel.
Parts of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
To achieve effective EDM, several key components and setups are involved. Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) is a remarkable machining process that utilizes electrical sparks to shape and machine various materials.
To better understand how EDM works, let’s explore the different parts of an EDM machine and their respective functions. By exploring these components, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of this innovative manufacturing technology.
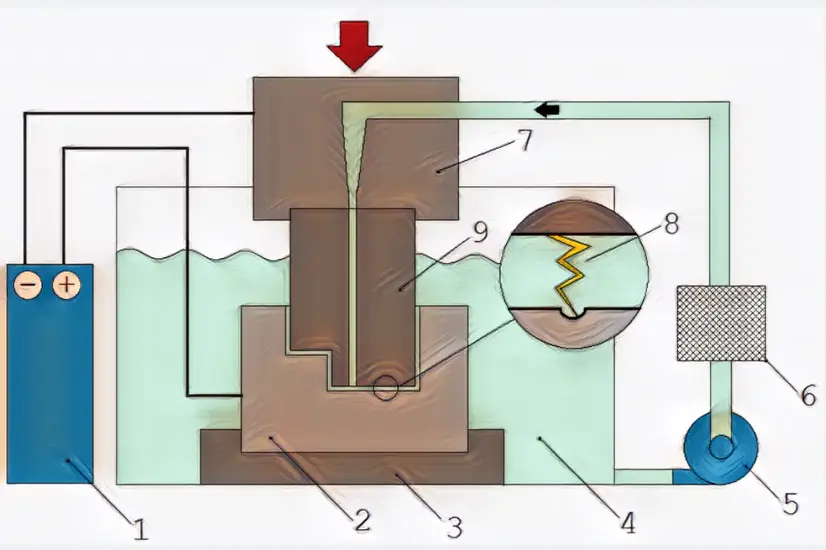
- DC Pulse Generator:
- The DC pulse generator is a key component of the Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) system that supplies electrical energy in the form of pulsed direct current (DC) to the electrode and workpiece. It controls the voltage and current characteristics of the electrical discharges, providing the necessary energy for material removal.
- Workpiece:
- The workpiece refers to the component or material being machined in the EDM process. It can be made of various materials, including metals and alloys. The workpiece is securely held in place on the worktable or fixture during machining, and its geometry and surface features are gradually shaped through the repeated electrical discharges.
- Fixture:
- A fixture is a device used to hold the workpiece in a stable and precise position during the EDM process. It ensures that the workpiece remains securely fixed and properly aligned with the electrode, allowing for accurate machining. The fixture may incorporate clamps, screws, or other mechanisms to hold the workpiece firmly in place.
- Dielectric Fluid:
- Dielectric fluid, also known as EDM oil or EDM fluid, is an electrically insulating liquid that surrounds the machining area in an EDM system. It serves several important functions: cooling the electrode and workpiece, flushing away debris and eroded material, and preventing electrical discharges from occurring outside the desired machining region. Common dielectric fluids include hydrocarbon-based oils and deionized water.
- Pump:
- A pump is used to circulate the dielectric fluid through the EDM system. It maintains a continuous flow of the fluid, ensuring efficient cooling, debris removal, and dielectric breakdown in the spark gap. The pump provides a steady supply of fresh dielectric fluid and helps maintain a consistent machining environment.
- Filter:
- A filter is incorporated into the EDM system to remove contaminants and particles from the dielectric fluid. It helps maintain the cleanliness of the fluid and extends its lifespan, ensuring optimal performance during the machining process. The filter traps debris and suspended particles, preventing them from interfering with the electrical discharges or clogging the system.
- Tool Holder:
- The tool holder is a component that securely holds the electrode in position during the EDM process. It allows for precise positioning and movement of the electrode relative to the workpiece. The tool holder may have adjustable settings to accommodate different electrode sizes, shapes, and orientations.
- Spark:
- The spark refers to the controlled electrical discharge that occurs between the electrode and the workpiece during the EDM process. It is generated through dielectric breakdown, forming a conductive plasma channel. The intense heat generated by the spark melts and vaporizes material from the workpiece, leading to material removal.
- Tool:
- In EDM, the tool refers to the electrode that shapes the workpiece. It can be made of copper or graphite due to their high electrical conductivity and erosion resistance. The tool’s geometry corresponds to the desired shape or feature to be machined on the workpiece. As electrical discharges occur, the tool gradually erodes the workpiece material, resulting in the desired shape or contour.
Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring accurate and efficient machining, allowing manufacturers to create intricate shapes, achieve tight tolerances, and work with challenging materials.
Choosing the right electrode material is crucial in EDM. Copper and graphite electrodes are commonly used due to their excellent electrical conductivity and erosion resistance.
Copper electrodes are often preferred for their high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for applications involving high power levels. Graphite electrodes, on the other hand, exhibit better wear resistance and are frequently used for fine finishing operations.
Working of Electrical Discharge Machining process
- When the electrode approaches the workpiece, a small gap is maintained between them, typically in the range of 0.001 to 0.01 mm. The power supply delivers short-duration pulses of high voltage and high current across this small gap.
- Dielectric Breakdown:
- The high voltage applied between the electrode and the workpiece causes dielectric breakdown of the surrounding fluid. This breakdown creates a conductive channel known as a plasma channel or spark channel. The plasma channel is highly ionized and allows the flow of current between the electrode and the workpiece.
- Material Removal:
- As the electrical discharge occurs, intense heat is generated within the plasma channel. The high temperature melts and vaporizes small particles of the workpiece material, which are then flushed away by the dielectric fluid. This process, known as electrical erosion, gradually removes material from the workpiece, shaping it according to the electrode’s contour.
- Repeated Discharge:
- The electrical discharge process is repeated multiple times, with each discharge removing a small amount of material. This repetitive action allows precise and controlled material removal, enabling the creation of complex shapes, intricate details, and fine finishes.
- Control Parameters:
- Several parameters are crucial for controlling the EDM process and achieving desired machining results. These parameters include pulse duration (typically ranging from 0.1 to 100 microseconds), pulse current, voltage, servo speed, and the gap between the electrode and the workpiece. Fine-tuning these parameters based on the material properties, desired surface finish, and machining requirements is crucial for achieving accurate and efficient results.
Applications of Electrical Discharge Machining
Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) finds widespread applications across multiple industries due to its unique capabilities and precision. In this section, we’ll explore some of the key industries that benefit from EDM and highlight specific applications within each sector.

- Automotive Industry:
EDM plays a vital role in the automotive industry, where precision and efficiency are paramount. Some common applications of EDM in automotive manufacturing include:
a. Injection Molds: EDM is used to produce high-precision injection molds for manufacturing plastic components like bumpers, dashboards, and interior parts. The intricate details and complex geometries required in these molds can be achieved with EDM’s precision.
b. Engine Components: EDM is employed to create intricate cooling channels in cylinder heads and other engine components. These channels help improve heat dissipation, enhancing engine performance and durability.
c. Gear Manufacturing: EDM is utilized to shape gears with high accuracy, especially in cases where traditional machining methods may not be suitable due to the hardness or complexity of the material. - Aerospace Industry:
Aerospace manufacturing demands precise and lightweight components, making EDM a valuable process. Some notable applications of EDM in aerospace include:
a. Turbine Blade Cooling Holes: Wire EDM is used to cut cooling holes in turbine blades, ensuring efficient heat dissipation and maintaining structural integrity.
b. Aerospace Molds and Dies: EDM is employed to create molds and dies for aerospace components, such as aircraft interiors, structural parts, and engine components. These molds require intricate details and high precision, which can be achieved through EDM. - Medical Device Production:
The medical device industry relies on EDM for the production of various critical components. Key applications include:
a. Implant Manufacturing: EDM is used to shape and refine implants such as hip replacements, spinal implants, and dental implants. The precision and surface finish achieved through EDM ensure proper fit and biocompatibility.
b. Surgical Tool Manufacturing: EDM is employed to produce complex surgical tools with fine details and sharp edges, enabling surgeons to perform intricate procedures accurately. - Electronics and Semiconductor Industries:
EDM is extensively used in the electronics and semiconductor sectors for intricate manufacturing processes. Examples of EDM applications in these industries include:
a. Microelectrode Fabrication: Micro-EDM is employed to create precise patterns on microelectrodes used in electronic devices and microfluidic systems.
b. Mold Cavities for Electronic Enclosures: EDM is used to produce precise mold cavities for electronic enclosures, ensuring proper fit and functionality of electronic components.
These are just a few examples of how Electrical Discharge Machining is utilized across various industries.
EDM’s ability to shape intricate geometries, work with challenging materials, and maintain high precision makes it a preferred choice in manufacturing processes where traditional methods fall short.
Since we’re talking about Traditional machining methods, let’s discuss about the differences between Traditional machining methods and Electrical Discharge Machining process.
Comparison between traditional machining processes and Electrical Discharge Machining process
| Aspect | Traditional Machining | Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) |
|---|---|---|
| Suitable Geometry | Limited to simple shapes | Suitable for complex geometries |
| Tolerances | Good for moderate tolerances | Excellent for tight tolerances |
| Material Capability | Limited to softer materials | Works with both soft and hard materials |
| Surface Finish | Typically requires post-finishing | Can achieve high-quality surface finish |
| Machining Time | Faster for simple shapes | Slower for complex geometries |
| Initial Investment | Lower initial setup cost | Higher initial setup cost |
| Tool Wear | Tool wear is significant | Minimal tool wear |
| Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) | May cause HAZ on certain materials | Minimal HAZ on workpiece |
| Complexity of Setup | Relatively simple setup process | Requires electrode design and setup |
| Design Flexibility | Limited by tool geometry | Offers high design flexibility |
| Use with Hardened Materials | Not suitable for hardened materials | Can effectively machine hardened materials |
| Efficiency with Intricate Shapes | Limited in creating intricate details | Can produce intricate details and sharp corners |
The Benefits of Electrical Discharge Machining:
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) offers a range of benefits that make it an indispensable tool in various manufacturing processes. However, like any machining technique, it also has its limitations.
- Precision and Accuracy:
- EDM is renowned for its exceptional precision, allowing for the creation of intricate and complex shapes with tight tolerances. It can achieve accuracies of up to a few micrometers, ensuring the production of high-quality components.
- Versatility with Materials:
- One of the significant advantages of EDM is its ability to work with a wide range of materials. From metals like steel, aluminum, and titanium to ceramics and even hardened tool steels, EDM can effectively shape and machine various materials, including those with high hardness and brittleness.
- Complex Geometries:
- EDM excels in producing components with intricate and complex geometries, such as cavities, slots, undercuts, and sharp corners. Unlike traditional machining methods, which may struggle with these features, EDM’s non-contact erosion process enables the creation of such intricate shapes with ease.
- Surface Finish:
- EDM can achieve excellent surface finishes, even on hard and challenging materials. With proper parameter control, it can produce surfaces with low roughness and minimal tool marks, eliminating the need for additional finishing operations in many cases.
- Heat and Stress Resistance:
- As EDM is a non-contact machining process, it minimizes the heat-affected zone (HAZ) and residual stresses on the workpiece. This characteristic is particularly advantageous when working with heat-sensitive materials or components that require minimal distortion.

Limitations and Considerations of Electrical Discharge Machining:
- Slower Material Removal Rate:
- Compared to conventional machining methods like milling or turning, EDM typically operates at a slower material removal rate. It excels in precision and intricacy rather than speed, making it more suitable for applications where precision is prioritized over production time.
- Cost:
- The initial investment for EDM equipment can be higher compared to conventional machining tools. Additionally, the cost of consumables like electrodes and dielectric fluids should be considered. However, the cost-effectiveness of EDM can still be favorable for certain applications that require its unique capabilities.
- Size and Weight Limitations:
- EDM is most commonly used for smaller to medium-sized components due to machine size limitations. Large and heavy workpieces may pose challenges in terms of machine capacity and handling.
- Design Constraints:
- EDM imposes certain design constraints due to its erosion-based nature. For instance, the presence of small radii or sharp internal corners may require additional electrode machining strategies or post-EDM finishing to achieve the desired results.
- Potential for Recast Layer and Surface Debris:
- During the EDM process, a recast layer can form on the machined surface, which may require additional cleaning or machining operations. Additionally, fine debris generated during erosion should be carefully managed to ensure the cleanliness and integrity of the final component.
By understanding the benefits and limitations of Electric Discharge Machining, manufacturers can effectively assess its suitability for their specific applications.
Discover More about some popular Manufacturing Techniques:
1. What is extrusion? detailed explanation with PDF
2. Rolling process – working, types, advantages, and applications with PDF
3. What is GMAW or MIG welding? with PDF
Advancements and Innovations in Electrical Discharge Machining
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) has continually evolved and embraced advancements that enhance its capabilities and make it more efficient.
- Emerging Trends in EDM Technology:
a. Additive Manufacturing and EDM: The combination of additive manufacturing (3D printing) and EDM has opened up new possibilities. EDM can be used to post-process 3D printed metal parts, refining their surface finish, and achieving precise dimensional accuracy. This synergy enables the production of complex geometries with high-quality surface finishes.
b. Micro-EDM: Micro-EDM involves machining on a microscale, with features as small as a few micrometers. It has found applications in microelectronics, microfluidics, and medical device manufacturing. For instance, micro-EDM is used to fabricate micro-molds for producing miniature plastic components and to create intricate patterns on microelectrodes for medical implants.
c. Hybrid Machining: Combining EDM with other machining processes, such as milling or grinding, has gained traction. Hybrid machining allows for the advantages of multiple processes to be leveraged in a single setup, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced production time. For example, the combination of EDM and milling can be used to produce cooling channels in mold cavities, maximizing heat dissipation during plastic injection molding. - Integration of EDM with Computer Numerical Control (CNC):
CNC technology popularized by CNC machines has revolutionized the manufacturing industry with the help of industrial automation. The integration of EDM with CNC systems enables precise control and manipulation of the electrode’s movements, resulting in improved accuracy and repeatability.
CNC-guided EDM machines can execute complex tool paths and automated tool changes, further enhancing productivity and reducing manual intervention.
Discover more about some highly advanced CNC machines available today like the 5-axis CNC machine and the Top 10 CNC Machine manufacturers & brands - Automation and Robotics in EDM Processes:
Automation and robotics have made significant contributions to the efficiency and productivity of EDM. Robotic systems are employed for tasks such as electrode and workpiece handling, tool changing, and part loading/unloading.
This integration minimizes human intervention, reduces setup times, and allows for continuous operation, even during non-working hours. Automation also enhances safety by keeping operators away from hazardous environments.

For example, in the automotive industry, EDM robotic cells are used for the production of engine components, such as cylinder heads and transmission parts. The robotic system handles the electrodes and workpieces, ensuring precise alignment and consistent quality throughout the machining process.
These advancements and innovations in Electric Discharge Machining have paved the way for more efficient, accurate, and flexible manufacturing processes.
By embracing emerging trends, integrating with CNC, and leveraging automation, EDM has become an indispensable tool in industries ranging from aerospace to medical devices, where intricate geometries and high-quality surface finishes are essential.
Optimizing the Electrical Discharge Machining Process: Tips and Considerations
To make the most of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) and ensure successful implementation, it’s essential to optimize the process and consider various factors that can enhance efficiency and productivity. In this section, we’ll provide you with practical tips and considerations to help you harness the full potential of EDM.
- Material Selection:
- When choosing materials for EDM, consider their conductivity, hardness, and machinability. Conductive materials like steel, copper, and graphite are well-suited for EDM. Hardened materials can be machined effectively using EDM, but it’s important to balance material hardness with electrode wear and machining time.
- Electrode Selection:
- Selecting the right electrode material is crucial for achieving desired results. Copper and graphite electrodes are commonly used due to their excellent electrical conductivity and erosion resistance. Copper electrodes are preferred for high power applications, while graphite electrodes offer superior wear resistance for fine finishing operations.
- Parameter Optimization:
- Proper control of EDM parameters, such as pulse duration, current, voltage, and servo speed, is crucial for achieving desired machining results. Fine-tuning these parameters based on the material, geometry, and surface finish requirements is essential. Manufacturers often conduct parameter experiments and utilize specialized software or expert knowledge to optimize the process.
- Dielectric Fluid Selection:
- The choice of dielectric fluid depends on factors such as machining speed, surface finish requirements, and material being machined. Common dielectric fluids include hydrocarbon-based oils, deionized water, and synthetic dielectric fluids. Consider factors like flushing efficiency, electrode wear, and the dielectric’s ability to suppress sparks during the EDM process.
- Workpiece Fixturing and Stability:
- Proper workpiece fixturing and stability are crucial for achieving accurate and repeatable results. Securely clamp the workpiece to minimize vibration or movement during machining. Consider the workpiece material, geometry, and size to determine the most appropriate fixturing strategy.
- Tool Path Generation:
- When creating tool paths for EDM, take into account the desired shape, surface finish requirements, and electrode wear. Utilize computer-aided design (CAD) software or dedicated CAM (computer-aided manufacturing) systems to generate tool paths that optimize material removal, minimize electrode wear, and achieve desired surface finishes.
- Maintenance and Cleaning:
- Regular maintenance of the EDM machine, including electrode and dielectric fluid replacement, is essential to ensure consistent performance. Cleaning the machine, filters, and removing debris helps maintain the integrity of the machining environment and prolong the life of the equipment.
- Safety Considerations:
- Like any machining process, EDM involves certain safety considerations. Ensure proper training for operators and adhere to safety protocols, including wearing personal protective equipment (PPE), handling electrodes and workpieces with care, and following proper machine shutdown and maintenance procedures.
By considering these tips and optimizing the Electrical Discharge Machining process, you can achieve enhanced productivity, improved surface finishes, and consistent machining results.
Case Study: Manufacturing a Precision Mold Cavity Using Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
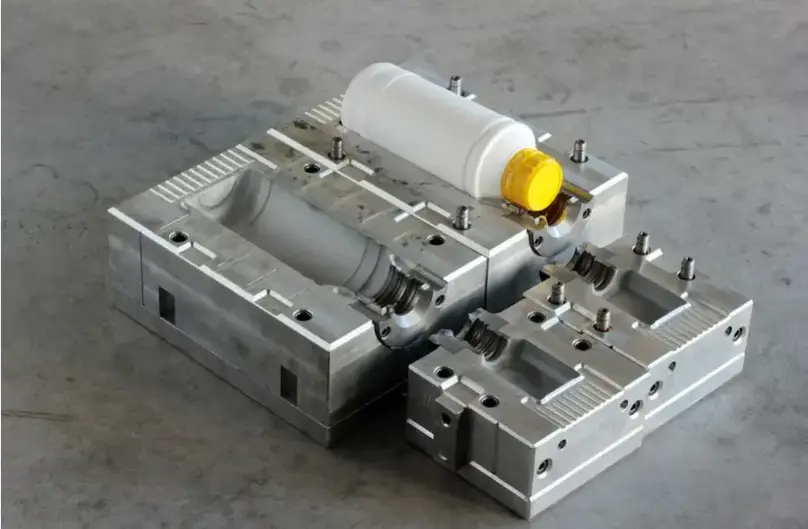
Introduction to case study:
In this case study, we will explore the manufacturing process of a precision mold cavity using Electric Discharge Machining (EDM). We will discuss the selection criteria for utilizing EDM, the setup of an EDM machine for this specific application, and the advantages and limitations of using EDM in this context.
Component Selection Criteria:
The selection of EDM for manufacturing a precision mold cavity is driven by several factors, including the complexity of the cavity’s geometry, the need for high precision, and the hardness of the material being machined.
EDM is well-suited for producing intricate mold cavities with fine details, such as those required for injection molding of plastic components. It allows for the creation of complex shapes, sharp corners, and small radii that may be challenging to achieve with conventional machining methods.
Additionally, if the mold material is hardened tool steel or other difficult-to-machine materials, EDM offers a viable solution due to its ability to work with such materials effectively.
EDM Machine Setup:
To manufacture the precision mold cavity, a CNC-controlled EDM machine will be used. The setup process involves the following steps:
- Material Preparation:
- Select a suitable material for the mold cavity, such as hardened tool steel. Prepare the workpiece by ensuring it is clean, securely fixtured, and positioned accurately on the machine’s worktable.
- Electrode Selection:
- Choose an appropriate electrode material based on the workpiece material, surface finish requirements, and electrode wear considerations. Copper or graphite electrodes are commonly used for EDM, with graphite offering better wear resistance for fine finishing operations.
- Electrode Design and Machining:
- Design the electrode based on the mold cavity specifications and generate the electrode geometry using CAD software. Utilize EDM-specific CAM software to generate the tool path for machining the electrode. Set up the EDM machine to accurately machine the electrode to the desired shape.
- EDM Process Parameters:
- Optimize the EDM process parameters, including pulse duration, current, voltage, and servo speed, to achieve the desired surface finish, dimensional accuracy, and electrode wear. Conduct parameter experiments and fine-tune the settings based on the specific material and geometry of the mold cavity.
- EDM Machining:
- Start the EDM machining process by initiating the electrical discharge between the electrode and the workpiece. Control the EDM parameters and the movement of the electrode to erode the workpiece material and shape the mold cavity accurately. Employ proper dielectric fluid for efficient flushing and debris removal during machining.
Advantages of Using EDM for Precision Mold Cavity Manufacturing:
- Complex Geometry: EDM enables the production of intricate and complex mold cavity geometries, including undercuts, thin ribs, and small features that are challenging to achieve with conventional machining methods.
- High Precision: EDM offers exceptional accuracy, allowing for tight tolerances and precise replication of the mold cavity geometry.
- Hardened Material Capability: EDM can effectively machine hardened materials like tool steels, enabling the production of durable mold cavities with excellent wear resistance.
- Surface Finish: EDM can achieve high-quality surface finishes, reducing the need for additional finishing operations and improving the performance of the injection molding process.
Limitations of Using EDM for Precision Mold Cavity Manufacturing:
- Machining Time: EDM typically operates at a slower material removal rate compared to conventional machining methods, which may result in longer machining times for complex mold cavities.
- Initial Investment: Setting up an EDM machine, including the required tooling and equipment, may involve a higher initial investment compared to some other machining processes.
- Design Constraints: EDM imposes certain design constraints due to the erosion-based nature of the process. Sharp internal corners, small radii, or certain geometries may require additional electrode machining strategies or post-EDM finishing operations to achieve the desired results.
Case Study Conclusion:
Manufacturing a precision mold cavity using Electric Discharge Machining (EDM) offers significant advantages in terms of producing complex geometries, achieving high precision, and working with hardened materials.
By carefully selecting the appropriate material, optimizing the EDM process parameters, and utilizing advanced EDM machine setups, manufacturers can create mold cavities that meet the stringent requirements of injection molding applications. While EDM may have limitations in terms of machining time and initial investment, its unique capabilities make it a valuable technique for producing precision components like mold cavities.
We recommend watching this 1.5 minute long video (not sponsored):
Closing Thoughts
We’ve covered a comprehensive range of information on Electrical Discharge Machining, from its principles and applications to the benefits, limitations, and optimization strategies. With this knowledge, you’re equipped to explore the world of EDM and harness its potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and inspired you to delve further into the realm of Electric Discharge Machining. Embrace the possibilities, innovate, and continue pushing the boundaries of precision manufacturing.
That’s an overview of Electric discharge machining. If you like this post or have any suggestions do let us know in the comments we would love to hear from you.
References:
- B. Denkena, et al. “Electric Discharge Machining (EDM).” Machining of Hard Materials. Springer, Cham, 2018.
- M. Brandt, et al. “The Fundamentals of Electrical Discharge Machining.” CIRP Annals – Manufacturing Technology, vol. 59, no. 2, 2010, pp. 760-777.
- K. K. Karunakaran, et al. “Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Design, Development, and Performance Analysis.” Materials and Manufacturing Processes, vol. 34, no. 2, 2019, pp. 121-136.
Share The Mechanical post with your mates and colleagues, so that we can keep producing such content for FREE!!





