What is meant by 3, 4, 5, and 6-Axis CNC Machining?
This is a 3 axis or a 5 axis CNC machine! You might have heard someone saying this. Ever wondered what is meant by 3, 4, or a 5 axis CNC machine?
Well, you have come to the right place, this is The Mechanical post and today we are going to discuss the different CNC machine axes.
You can download the PDF on Different CNC machine axes at the end of this article. This article is written by Peter Jacobs from CNCmasters.com These people are in business since 1990 so you know that you’re learning from the experts. More about the author at the end of the article.
Introduction

Milling is one of the most crucial techniques employed in CNC precision machining with applications ranging from mechanical components and medical to aerospace, optical, automobile, and more. Rotary cutters are employed in the milling process to remove material from a workpiece. This process gets executed by fixing the workpiece at an angle to the axis of the tool.
At the heart of these sophisticated machines lie the CNC machine axes, which form the foundation of their precise movements and operations. Understanding the working of the different types of CNC machine axes is essential for engineers, operators, and manufacturers seeking to harness the full potential of these cutting-edge systems.
This comprehensive guide aims to provide a technical and professional exploration of CNC machine axes, specifically focusing on the commonly encountered configurations of 3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis, and 6-axis systems.
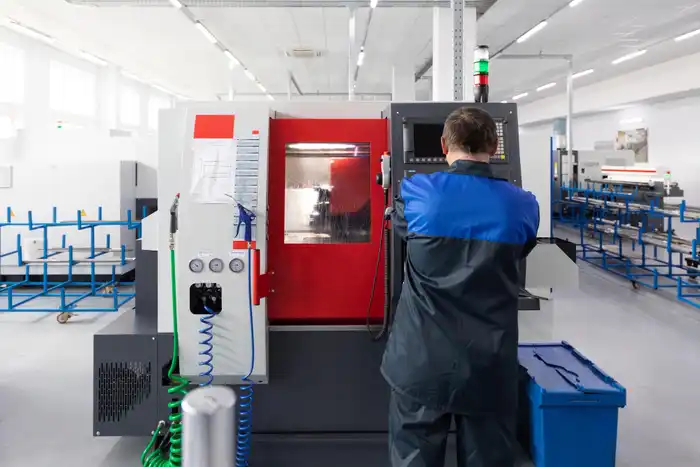

By delving into the nuances of these axis setups, we will uncover the distinct capabilities, advantages, and considerations associated with each configuration.
If you are in a hurry, here’s a brief answer to what are 3, 4, 5, and 6-axis in CNC machines?
3-Axis CNC machines utilize X, Y, and Z axes to perform precise movements in three-dimensional space, making them ideal for flat surfaces and simple geometries.
4-Axis CNC machines introduce an additional rotational axis (A-axis) that enables the machine to rotate the workpiece, unlocking capabilities for indexing and contouring operations.
5-Axis CNC machine go further with a fifth axis (B-axis), enabling simultaneous and positional movements, allowing for complex, curved surfaces and eliminating the need for multiple setups.
6-Axis CNC machines add a sixth rotational axis (C-axis), empowering multi-sided machining, intricate features, and compound angles for unparalleled precision and versatility.
Detailed explanation of 3, 4, 5, and 6 Axis CNC Machines
The 3-Axis CNC Machine

The 3 axis CNC Machines contain only linear axes, namely:
| Axis | Movement |
|---|---|
| X | Left & Right Linear Motion |
| Y | Front & Back Linear Motion |
| Z | Depth (Up and Down) |
With their linear axes, 3-axis CNC machines perform a variety of operations with finesse. They excel at tasks that require straightforward, linear motions, such as milling flat surfaces, drilling holes, and cutting simple profiles. The coordinated movements of the X, Y, and Z axes ensure precise positioning and consistent results, making 3-axis machines reliable workhorses.
3-axis machining involves the workpiece remaining still with only the cutting tool traversing along the three axes to mill the part. 3-axis machines have applications in the case of machining 2D and 2.5D geometry.
Since 3-axis machining only operates on the three axes, the process becomes relatively simple and enables removing the material in these three axes described by back to front, side to side, and up and down.
The 3-axis milling has its limitations and thus cannot be used to design features on an angle to the X-Y-Z coordinate system, regardless of the feature being planar.
Advantages of 3 axis CNC machines:
- Simplicity and ease of use.
- Cost-effective solution for many machining applications as compared to others.
- Versatile for a wide range of industries.
- Ideal for flat surfaces and simpler geometries.
- Reliable and widely available in the market.
Limitations of 3-Axis CNC Machines:
- Inability to perform complex multi-sided machining.
- Limited access to difficult-to-reach areas on intricate workpieces.
- Requires multiple setups for machining operations from different angles.
- Not suitable for highly intricate or complex part geometries.
Applications of 3 axis CNC machine
The 3-axis machine is best suited for:
- Woodworking: Creating cabinetry, furniture components, and decorative elements.
- Sign Making: Carving letters and shapes for signage and displays.
- Prototyping: Fabricating concept models and functional prototypes.
- Metalworking: Milling flat surfaces, drilling holes, and cutting simple profiles.
What is a 4-Axis CNC Machine?
Introduction to the Fourth Axis: Unleashing Rotary Power
Say hello to the fourth axis, typically represented by the A-axis. Apart from the 3 linear axes, X, Y and Z, the A axis in CNC Machine is the axis of rotation around the X axis.
This rotational addition to the CNC machine opens doors to dynamic machining operations. By enabling the workpiece or cutting tool to rotate around a specific axis, 4-axis CNC machines expand their repertoire of movements, bringing enhanced flexibility and precision to the manufacturing process.
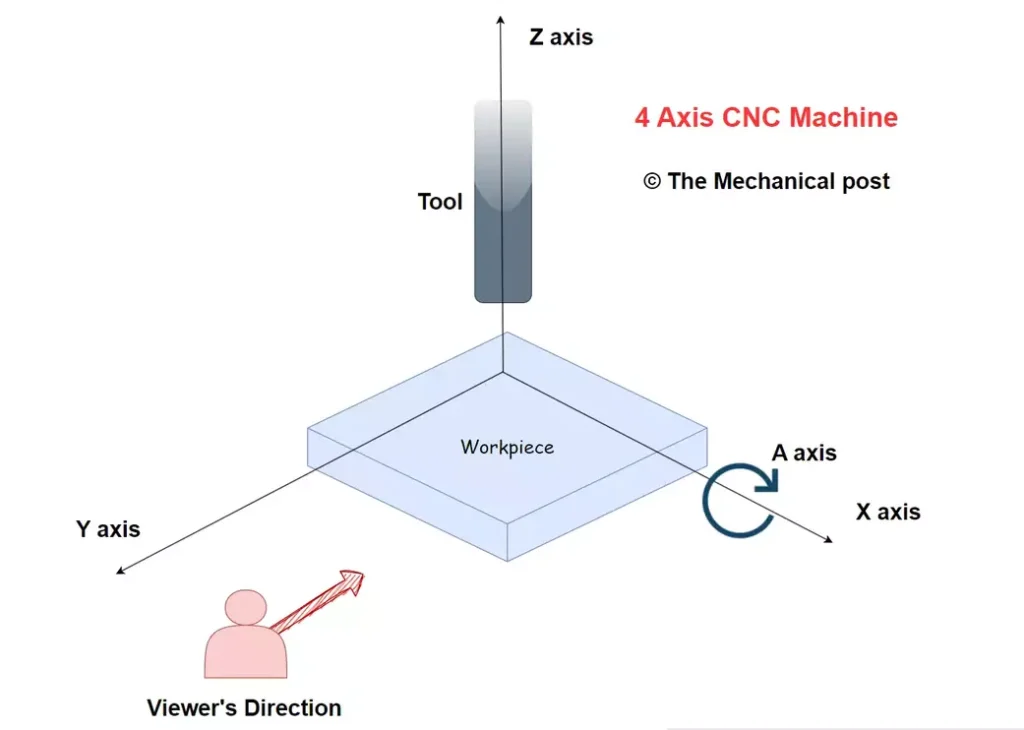
| Axis | Movement |
|---|---|
| X | Left & Right Linear Motion |
| Y | Front & Back Linear Motion |
| Z | Depth (Up and Down) |
| A | Rotation about X axis |
Benefits and Expanded Capabilities: A New Dimension of Machining
With the inclusion of the fourth axis, 4-axis CNC machines can tackle complex machining tasks with finesse. They excel in operations that require indexing, contouring, and continuous rotations, allowing for the creation of curved surfaces, intricate engravings, and sculpted designs.
The ability to position the workpiece at different angles enhances accessibility to various surfaces, reducing the need for repositioning and minimizing setup time.
Rotary Table and Indexing Operations: Unlocking Precision and Versatility
One of the key components enabling the fourth axis functionality is the rotary table. This mechanical marvel acts as a platform that can rotate the workpiece precisely, opening up a world of possibilities for intricate machining operations.
Indexing, a technique used in 4-axis machining, involves rotating the workpiece in fixed increments, allowing for precise cuts and complex geometries.
These indexing operations provide the ability to create detailed patterns, flutes, and intricate textures on cylindrical or curved surfaces.
Case Studies Highlighting Applications of 4-Axis CNC Machines
To truly grasp the potential of 4-axis CNC machines, let’s explore some real-world applications. In the aerospace industry, these machines are invaluable for manufacturing turbine blades with intricate airfoil profiles, precisely carved contours, and cooling channels.
In the realm of artistic craftsmanship, 4-axis systems enable the creation of exquisite sculptures, ornate moldings, and detailed reliefs. Furthermore, the production of gears, cams, and other complex components greatly benefits from the multi-axis capabilities of 4-axis CNC machines.
With the capabilities and applications of 4-axis CNC machines now unveiled, we’re poised to take the plunge into the next dimension.
Mostly, the workpiece will get rotated to facilitate the cutting process around the A-axis. 4-axis milling is implemented when holes and cut-outs must be made around a cylinder or the side of a piece.
Advantages of 4 axis CNC machines:
- Enhanced versatility for machining complex geometries and curved surfaces.
- Ability to perform indexing and contouring operations, enabling precise cuts from multiple angles.
- Reduced setup time by eliminating the need for multiple repositioning of workpieces.
- Improved access to hard-to-reach areas of the workpiece.
- Expanded capabilities for tasks such as engraving, fluting, and creating intricate designs.
Limitations of 4-Axis CNC Machines:
- Complexity in programming and operation compared to 3-axis machines.
- Increased mechanical complexity and potential reduction in machine rigidity.
- Higher upfront cost and maintenance requirements compared to 3-axis machines.
- May require specialized software and skilled personnel for optimal utilization.
Applications of 4 axis CNC machine
The 4-axis machine is best suited for:
- Aerospace: Manufacturing turbine blades, engine components, and complex aerospace structures.
- Automotive: Creating intricate molds, producing complex car body parts, and machining engine components.
- Sculpting and Artistic Industries: Sculpting intricate designs, creating decorative pieces, and producing customized artwork.
- Prototyping: Building functional prototypes with curved or multi-sided features that require precise machining operations.
What is a 5-Axis CNC Machine?
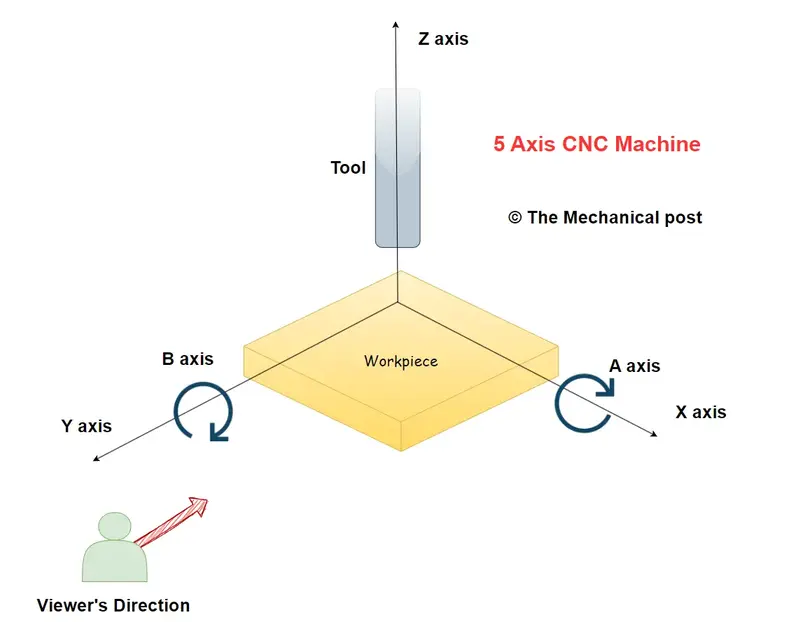
| Axis | Movement |
|---|---|
| X | Left & Right Linear Motion |
| Y | Front & Back Linear Motion |
| Z | Depth (Up and Down) |
| A | Rotation about X axis |
| B | Rotation about Y axis |
Introduction to the Fifth Axis: Unlocking Multi-Angle Machining
Introducing the fifth axis, commonly represented by the B-axis, which joins the X, Y, Z, and A axes in a symphony of machining excellence.
The inclusion of this rotational axis provides the ability to tilt the cutting tool or workpiece, enabling the CNC machine to reach multiple angles and orientations.
With the fifth axis, 5-axis CNC machines break free from the constraints of simple linear and rotational movements, venturing into the realm of simultaneous and positional machining.
5-axis machining covers all the axes of 4-axis machining alongside yet another rotational axis.
Simultaneous and Positional Machining: Beyond the Limits of Traditional Axes
Simultaneous machining is the hallmark of 5-axis CNC machines. This capability allows the cutting tool to move along multiple axes simultaneously, resulting in complex curved surfaces, sculpted contours, and intricate details.
By dynamically adjusting the position and orientation of the tool, 5-axis systems effortlessly navigate around the workpiece, eliminating the need for multiple setups and reducing machining time.
Positional machining, on the other hand, involves fixing the tool at a specific angle while maneuvering the workpiece. This approach is particularly useful when working on surfaces that require consistent tool contact, such as undercuts or inclined features. By adjusting the position of the workpiece, 5-axis CNC machines achieve optimal access to various surfaces, resulting in higher accuracy and quality

This machining technique can deliver intricate parts, which are critical for high-level such as including aerospace applications.
5-axis machining offers the option for single-step machining (reducing lead time), boosting the convenience of access to the part geometry, and enhancing the tool life and process efficiency by having the table tilted for the optimal cutting position.
5-axis machining is beneficial when a great degree of intricacy and precision is required.
Advantages of 5 axis CNC machines:
- Increased machining capabilities for complex and contoured geometries.
- Enhanced precision and accuracy due to simultaneous multi-axis movements.
- Reduction in setup time and improved efficiency by machining from multiple angles in a single operation.
- Ability to achieve smooth and seamless transitions between different surfaces.
- Expanded range of applications across industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and mold-making, among others.
Limitations of 5-Axis CNC Machines:
- Higher upfront cost and investment compared to lower-axis machines.
- More complex programming and setup requirements, requiring skilled operators.
- Potential for increased machine complexity, leading to higher maintenance and calibration needs.
- Limited workspace capacity due to the additional range of motion of the rotary axes.
- Increased complexity may lead to longer programming and machining times for certain operations.
Applications of 5 axis CNC machine
This 5 axis CNC machine is used for:
- Aerospace Industry: Manufacturing complex aircraft components, turbine blades, and engine parts with intricate contours.
- Automotive Industry: Producing complex car body parts, molds, and engine components requiring multi-axis machining.
- Medical Industry: Creating orthopedic implants, prosthetics, and surgical instruments with intricate geometries.
- Tool and Die Industry: Machining intricate molds, dies, and tooling for various applications.
- Artistic and Sculpting Industries: Crafting sculptures, statues, and artistic pieces with intricate designs and curved surfaces.
- High-precision Machining: Achieving tight tolerances and precision on intricate components such as gears and impellers.
- Prototyping: Developing functional prototypes with complex geometries and precise features for testing and validation.
Difference between 3 axis and 5 axis CNC machine:
| Aspect | 3-Axis CNC Machines | 5-Axis CNC Machines |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Axes | Three linear axes (X, Y, Z) | Five axes (X, Y, Z, A, B) |
| Machining Capabilities | Suitable for flat surfaces and simple profiles | Can handle complex and contoured geometries |
| Access to Hard-to-Reach Areas | Limited access to intricate or complex surfaces | Improved access to challenging surfaces and features |
| Setup Time | May require multiple setups for different angles | Reduced setup time with machining from multiple angles |
| Precision and Accuracy | Reliable precision for many machining applications | Enhanced precision and seamless surface transitions |
| Programming Complexity | Relatively simpler programming and operation | More complex programming and setup requirements |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost and maintenance compared to 5-axis | Higher upfront cost and investment |
You might also like to read:
6-Axis CNC Machining
The 6-axis machining process is similar to the 5-axis; however, it features an additional rotation axis about the Z-axis which can substantially boost speeds compared to 5-axis configurations.
A 6-axis machine has the potential of converting the raw metal bars into the final product by turning from both ends of the fixture with no flaws in the manufactured part. 6-axis milling is an efficient solution, primarily for the components that are intricate and demand unmatched precision.
6-axis CNC machines facilitate some arduous tasks such as drilling holes of various diameters and providing different speeds and cutting patterns. The final product quality delivered by a 6-axis machine is the best amongst all other CNC machines.

The 6-axis machines are typically utilized for volume machining of steel, cast iron, aluminum, and model-making materials.
Check out this informative video by CNC Titans on different machining axes. (*not sponsored)
Key Takeaways from this article:
- CNC machines offer various axis configurations, including 3-axis, 4-axis, 5-axis, and 6-axis, each with its own advantages and limitations.
- A 3-axis CNC machines provide simplicity, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, suitable for flat surfaces and simpler geometries.
- Advancing to 4-axis machines introduces indexing and contouring capabilities, expanding the potential for complex geometries.
- The 5-axis CNC machines offer simultaneous and positional machining, enabling intricate and curved surface production with enhanced precision.
- The 6-axis CNC machines push the boundaries further, enabling multi-sided machining and complex part creation.
- Each axis configuration finds applications in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and artistic fields.
- Consider factors like machining requirements, complexity, precision, and budget when selecting the appropriate CNC machine.
- The right axis configuration empowers manufacturers to achieve exceptional results, drive innovation, and stay ahead in the realm of precision manufacturing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, CNC machines have revolutionized the world of precision manufacturing, offering a wide range of axis configurations to suit various needs. The 3-axis CNC machines provide simplicity, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. Advancing to 4-axis machines introduces a new dimension of indexing and contouring operations, expanding capabilities for complex geometries.
Stepping further, 5-axis CNC machines unlock the potential for simultaneous and positional machining, enabling intricate and curved surface production with exceptional precision.
Lastly, the pinnacle of multi-axis machining lies in 6-axis CNC machines, empowering multi-sided machining and complex part creation.
From aerospace to automotive, medical to artistic industries, each axis configuration offers its own advantages and limitations. It is crucial for manufacturers and engineers to carefully consider their specific requirements and the intricacies of each axis configuration to select the most suitable CNC machine for their applications. With the right choice, they can unlock the full potential of precision machining

About the Author:
Peter Jacobs is the Senior Director of Marketing at CNC Masters. He is actively involved in manufacturing processes and regularly contributes his insights for various blogs in CNC machining, 3D printing, rapid tooling, injection molding, metal casting, and manufacturing in general.



![37 Must Have Workshop Tools & Their Uses with [PDF & Images]](https://mechanicalpost.site/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/tool-stoarge.webp)


Thank you for this article
Thanks, I’ve been looking for this for a long time, really helpful.
We’re glad to help you out. Let us know if you have any doubts