Screw thread: its terminology and types of screw threads with PDF
As Mechanical engineers, screws are a day-to-day part of our lives, we are surrounded by screws, and hence it is important to know about them. Be it from a ceiling fan to the smartphones or machines we use, they are almost everywhere in this modern world.
Today you would be reading about screws, terminology of screw threads, and types of screw threads.
Download your PDF on Screw thread terminology and its types at the end of the article.

What is a screw?
A screw is a helical groove cut on a cylindrical surface. It is a simple mechanical device that is used as a fastener to hold various parts together. A screw converts rotational motion into linear motion.
Advantages of screwed joints
- Screwed joints can be easily assembled and dismantled.
- Screwed joints are reliable in operation.
- Different types of screws are available depending upon the use.
- They have low cost due to standardization.
Disadvantages of screwed joints
- Welded joints are stronger than screwed joints.
- There is a problem with stress concentration in screws.
- Vibrations can loosen up the screwed joints.
Screw thread terminology
Given below are the various terms used for screw threads or the various elements of screw thread.
- Crest
- Root
- Flank
- Thread angle or Included angle
- Major diameter
- Minor diameter
- Depth of thread
- Pitch
- Pitch circle diameter
- Lead
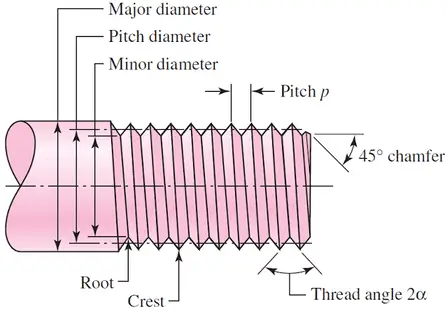
#1 Crest
The crest is the topmost part of the screw thread joining the 2 sides of a thread.
#2 Root
The root is the bottom formed between the 2 flanks of a thread.
#3 Flank
The flank is the part of a thread that connects the crest and the root.
#4 Thread angle or included angle
The thread angle or included angle is the angle made by two flanks of the thread.
#5 Major diameter
The major diameter of a screw thread is defined as the largest diameter of an external or internal screw thread.
For an external thread, the major diameter is the diameter of an imaginary coaxial cylinder that passes through the crests of external threads.
For an internal thread, the major diameter is the diameter of an imaginary coaxial cylinder passing through the roots of an internal thread.
#6 Minor diameter
The minor diameter of a screw thread is the smallest diameter of an external or internal screw thread.
In the case of an external thread, the minor diameter is the diameter of an imaginary coaxial cylinder passing through the roots of external threads.
In the case of an internal thread, the minor diameter is the diameter of an imaginary coaxial cylinder passing through the crests of internal threads.
#7 Depth of thread
The distance between the crest and the root of a screw thread when measured radially is known as the depth of the thread.
#8 Pitch circle diameter
The pitch circle diameter of a screw thread is the diameter of an imaginary cylinder that is coaxial with the screw axis which passes through the screw thread such that the width of the thread is equal to the width of the space in between.
#9 Pitch
The pitch of a screw thread is the axial distance from one point on a screw thread to the same point on the adjacent thread.
It can be the distance of either crest of one thread to the crest of the adjacent thread or the root of one thread to the adjacent root. The pitch is measured parallel to the thread axis.
#10 Lead
The linear distance advanced by the screw upon one complete rotation of the screw thread is known as the lead.
You might also want to read: Types of couplings and their uses with PDF
Types of screw thread profiles
The following are the different types of screw thread profiles:
- V thread.
- Whitworth thread.
- Square thread.
- Acme thread.
- Buttress thread.
1. V threads
V thread also known as the unified thread is a type of screw thread with a thread angle of 60 degrees. Also, as the name suggests, the shape of the cross-section of the thread profile is that of the letter V.
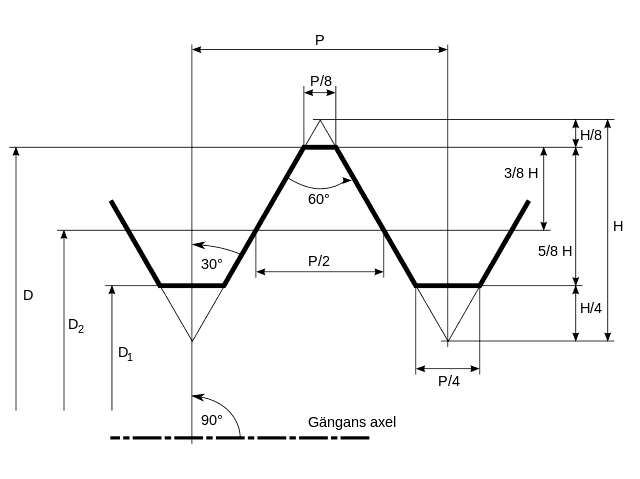
Mostly, fasteners like screws and bolts have V threads as it has low chances of loosening due to vibrations. V threads cause high friction between the surfaces and hence they are used in fasteners like screws and bolts.
Advantages of V threads
- V threads have high strength
- They have more load-carrying capacity than square threads.
- It is easy to manufacture on large scale.
- The production cost of V threads is low.
- V threads offer resistance while screwing and unscrewing due to high friction, hence they are used in fasteners.
Disadvantages of V threads
- V threads are less efficient due to high friction.
- The nut is subjected to radial or bursting pressure in V threads.
- V threads are not suitable for power transmission due to the high friction involved.
Applications of V thread
V threads have many applications which include fasteners, machine bolts, wood screws, etc.
You might also like to read:
2. Whitworth thread
Whitworth threads have a thread angle of 55° and have fillets at the crests and roots. Due to the fillet at the crests and roots, the strength of the threads is increased.
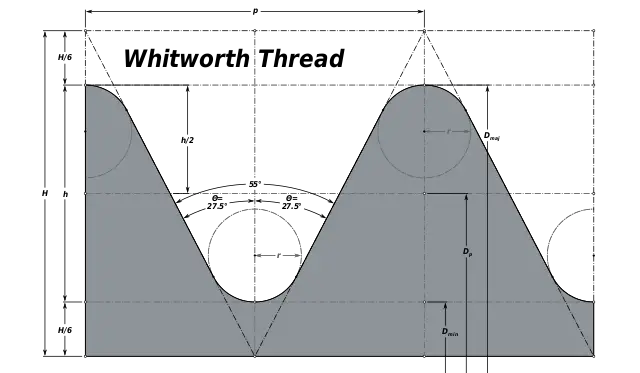
If p is the pitch, then the radius of the fillet of the BSW thread would be equal to 0.137329p. Whitworth threads were adopted as the British standard and were later known as BSW.
BSW stands for British Standard Whitworth.
The British standard Withworth was used on a large by the British for its navy and railways.
3. Square threads
Square threads are those types of screw threads whose cross-section when seen axially is in the form of a square.
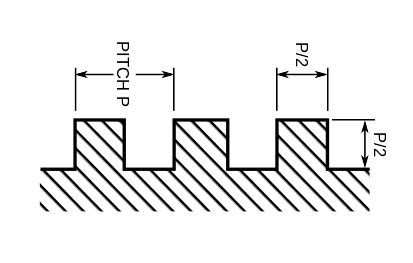
The square thread has a 0° thread angle, this is because the flanks of the square thread are perpendicular to each other.
Square thread is used for power transmission as they have the highest efficiency, hence it is used in power screws like screw jack, lead screw of a lathe, etc.
The depth of thread and thickness of thread is equal to half of the pitch (p/2). Square threads are used where power is to be transmitted in both directions.
Advantages of square thread
- Square threads have maximum transmission efficiency.
- It has a smooth and noiseless operation
- 0° thread angle results in no radial or bursting pressure on the nut.
- It can transmit power in both directions.
Limitations of square thread
- Square threads are difficult to manufacture.
- They are expensive to manufacture.
- Square threads are weaker than V threads.
- Load-carrying capacity is less when compared to V threads.
Applications of Square thread
The applications of square thread include power screws in screw jack, toggle jack, lead screw of lathe machine, etc.
4. Acme threads
Acme threads are a type of trapezoidal thread. It has an included angle/thread angle of 29° with the top (crest) being flat with the depth of thread equal to p/2 (where p = pitch).
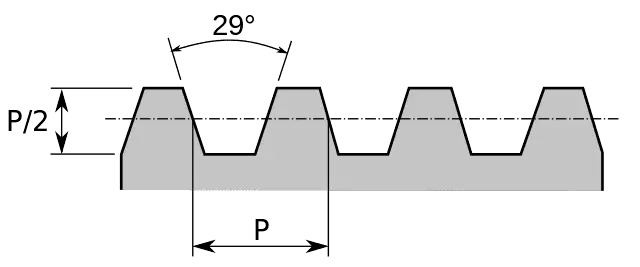
Acme threads can be easily cut by a single point cutting tool or by a die thus making it easy to manufacture acme threads.
Acme threads are wider at the base than square threads, which translates to increased strength and greater load-carrying capacity when compared to similar-sized square threads.
Acme threads are also used as power screws as they can transmit power in both directions.
Advantages of acme thread
- Acme threads are easy to manufacture as compared to square threads.
- It has more strength than square threads.
- It is easy to manufacture as compared to square thread.
- Acme threads are cheaper.
- Acme threads have more load-carrying capacity than square threads.
Limitations of acme threads
- Acme threads are less efficient than square threads.
- Due to the 29° thread angle, the thread exerts some bursting or radial pressure on the nut.
What is the difference between acme threads and square threads?
| Square threads | Acme threads |
|---|---|
| Square threads have a square profile. | Acme threads have a trapezoidal profile |
| Square threads have a thread angle/included angle of 0°. | Acme threads have a thread angle/included angle of 29°. |
| It has more efficiency. | It has comparatively less efficiency. |
| Square threads are difficult to manufacture. | Acme threads are easy to manufacture |
5. Buttress thread
Buttress thread is an unsymmetrical thread with an included / thread angle of 45°. A buttress thread is capable to withstand extreme axial loads in one direction only.
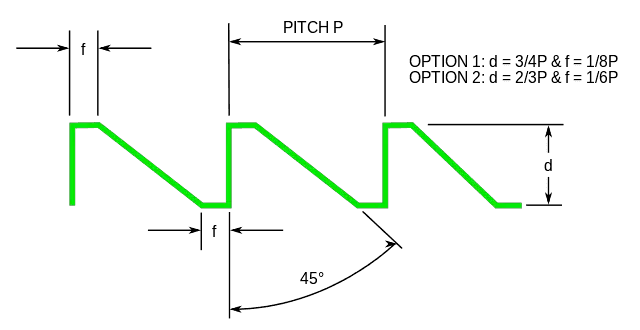
Buttress thread advantages
- Buttress threads have a high load-carrying capacity in 1 direction.
- It has good strength.
- Its efficiency can be compared with that of square threads.
- It can be economically manufactured.
Buttress thread disadvantages
- It can transmit power in one direction only.
Applications of buttress thread
The applications of buttress thread include vices, clamping devices, heavy lifting devices, etc where force is required to be applied in one direction only.
FAQ on Screw threads
1. What are right-hand threads and left-hand threads?
A right-handed thread is the one that tightens up when rotated in a clockwise direction. Whereas, a left-handed thread is the one that tightens up when rotated in the anti-clockwise direction.
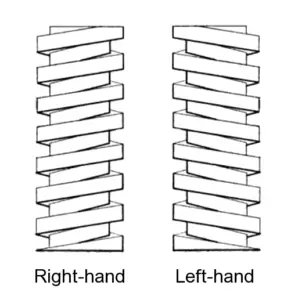
2. How to identify right-hand and left-hand threads?
The easiest way to identify right-hand and left-hand threads is by looking at the slope of the threads. If the slope of the thread rises towards the right it’s called a right-hand thread and if the slope rises towards the left, it’s known as a left-hand thread.
3. What is the thread angle of a square thread?
The square thread has a thread angle of 0°.
This brings us to the end of the article on Screw thread: its terminology and types. If you find this article helpful, do share it with fellow engineers and do consider dropping some likes on our Facebook page @TheMechanicalpost
Any doubts or queries? feel free to ask us in the comments. Till then keep learning!