CVT vs. Automatic Transmission: which is better?
As automobile enthusiasts, we know that the way power is transferred from the engine to the wheels can greatly impact the driving experience.
In this article, we will explore the world of transmissions and discover the nuances between two prominent contenders: the CVT (Continuously Variable Transmission) and the traditional Automatic Transmission (AT).
Transmissions have evolved over time, and the CVT represents the latest innovation in the automobile world. With its shiftless design and infinite gear ratios, the CVT has piqued the curiosity of drivers seeking a seamless and efficient driving experience. On the other hand, the tried-and-tested, true automatic transmission, with its hydraulic systems and gear sets, has long been the standard choice for many drivers.
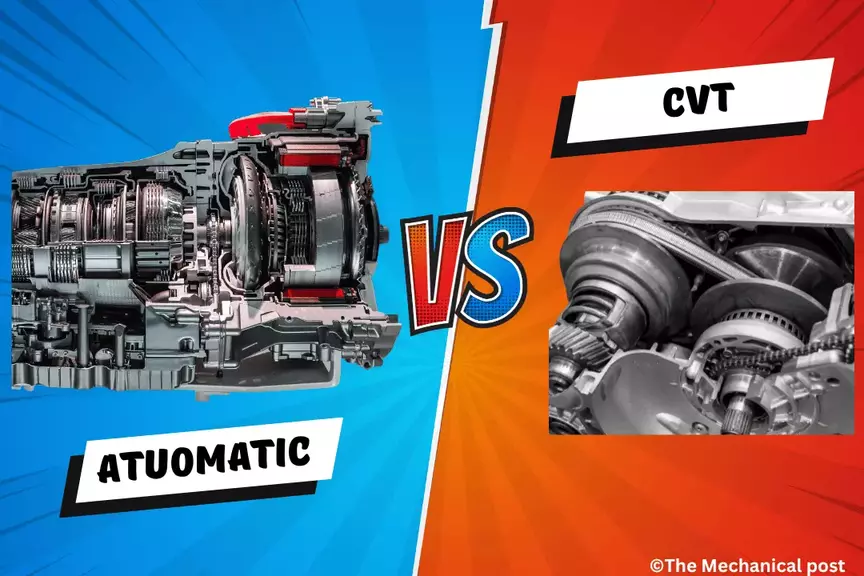
These differences between CVT and Automatic transmission systems goes beyond the realms of fuel efficiency and smoothness; it encompasses the thrill of acceleration, the art of gear changes, and the harmony between man and machine.
We have divided the differences between CVT vs. Automatic transmission into 2 parts i.e.
1. Technical differences
2. Differences important from a buyer’s perspective
So, buckle up and join us on this exploration as we unravel the intricate workings of CVT and automatic transmissions, allowing you to make an informed decision that aligns with your driving desires.
Understanding CVT Transmission
As we venture deeper into the realm of transmissions, let us unravel the mysteries of the Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT). This state-of-the-art technology replaces the conventional fixed gears with a system that seamlessly adjusts gear ratios for optimal performance.

The CVT operates through a pulley and belt system, eschewing the limitations of fixed gears. With its ability to provide an infinite range of gear ratios, the CVT ensures the engine operates at its most efficient RPM, resulting in enhanced fuel economy.
Toyota has even introduced a new innovation called the Launch Gear, which simulates the feeling of a conventional transmission’s first gear. This intelligent integration combines the benefits of both worlds, delivering improved performance while preserving the efficiency and smoothness characteristic of CVTs.
Discover more about What is CVT Transmission and how does it work? wherein we explore in detail about this amazing automobile part.
What is an Automatic Transmission?
Let us now shift our attention to the venerable Automatic Transmission (AT), a stalwart of the automotive world.
While the CVT may be the new kid on the block, the AT has long been the trusted companion of drivers worldwide.
Automatic transmissions employ a complex hydraulic system and gear sets to seamlessly adjust gear ratios based on driving conditions. The driver is treated to the sensation of gear changes without the need for manual intervention, allowing for a more connected and engaging driving experience.
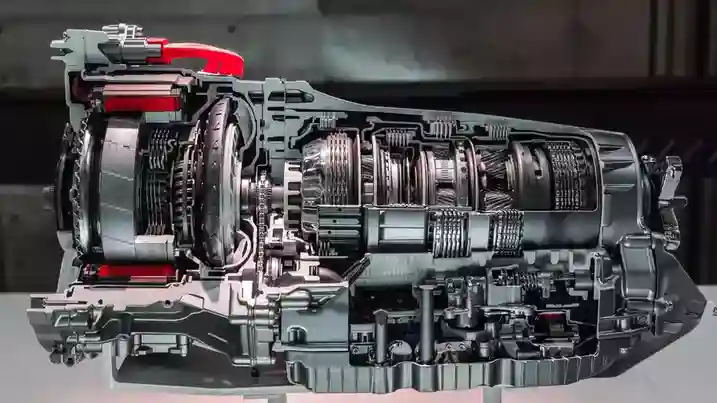
While ATs may not match CVTs in terms of fuel efficiency, their performance-oriented nature appeals to enthusiasts seeking that exhilarating acceleration and precise gear shifting. Climbing hills and conquering challenging terrain becomes a symphony of power and control as the automatic transmission expertly finds the ideal gear to keep you in the driver’s seat.
Join us as we delve into the inner workings of automatic transmissions, uncovering the magic behind their gear changes, and appreciating the dynamic driving experiences they bring to the table.
CVT vs. Automatic transmission:
Let’s compare CVT and automatic transmissions based on their technical aspects.
| Sr. no | CVT Transmission | Automatic Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Utilizes a pulley and belt system, offering an infinite number of gear ratios for optimal engine performance. | Relies on a set number of gears, each with fixed ratios, to achieve different speeds and torque outputs. |
| 2 | Transfers power smoothly and continuously, eliminating the need for traditional gear shifts and resulting in seamless acceleration. | Changes gears by disengaging one set of gears and engaging another, leading to noticeable gear shifts during acceleration. |
| 3 | Allows the engine to operate at its most efficient RPM, optimizing fuel economy and delivering improved gas mileage. | Experiences energy losses during gear shifts, which can impact fuel efficiency and result in lower overall MPG. |
| 4 | Offers better adaptability to different driving conditions, continuously adjusting gear ratios to match the engine’s power output and load requirements. | Requires gear changes to match specific driving conditions, making it less adaptable in real-time without manual intervention. |
| 5 | Lacks the distinct gear steps found in automatic transmissions, providing a more linear power delivery and smoother operation. | Delivers power in discrete steps due to gear changes, resulting in a more noticeable and segmented power delivery. |
| 6 | Often lighter in weight compared to automatic transmissions, contributing to improved fuel efficiency and reduced vehicle weight. | Typically heavier due to the additional components required for gear selection and engagement. |
| 7 | Can sometimes exhibit a “rubber band” effect, where the engine revs higher without a corresponding increase in vehicle speed during sudden acceleration. | Allows for a more immediate and responsive power delivery, with a direct correlation between engine RPM and vehicle speed. |
| 8 | Requires less frequent maintenance, as there are no physical gears that need to be serviced or replaced over time. | May require regular maintenance, such as fluid changes and periodic gear inspections, to ensure proper operation and longevity. |
| 9 | Offers a quieter operation, as the absence of gear changes reduces noise and vibrations associated with shifting gears. | May produce more noticeable noise and vibrations during gear changes, especially in older or less-refined automatic transmissions. |
| 10 | Provides a simpler mechanical design with fewer moving parts, potentially resulting in increased reliability and reduced mechanical failures. | Contains a more complex mechanical design, with multiple gears, clutches, and hydraulic systems, which may increase the likelihood of mechanical issues. |
| 11 | Can be more challenging to modify or upgrade due to the intricate nature of the CVT system and limited aftermarket support. | Offers greater flexibility for modifications and upgrades, with a wide range of aftermarket options available for various automatic transmission components. |
You might like to learn more about:
17 Best Track Cars you can buy Today
Difference between Disc and Drum Brake
25+ Different Types of Engines found in cars

Difference between CVT transmission and Automatic transmission from a buyer’s perspective:
We compared the pros and cons in a technical manner in the above table, now let’s take a look at the differences between them from a car buyer’s perspective to help you out with deciding which transmission suits you the best.
| Sr.no | CVT Transmission | Automatic Transmission |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Generally provides a smoother driving experience with seamless acceleration, which can enhance passenger comfort. | Offers a more traditional driving experience with distinct gear shifts, which some drivers may prefer for a sportier feel. |
| 2 | Known for improved fuel efficiency, making it an attractive choice for those seeking better mileage and reduced fuel costs. | May have lower fuel efficiency compared to CVTs due to energy loss during gear shifts, although modern automatic transmissions have improved in this aspect. |
| 3 | CVTs are often associated with a quieter operation, as the absence of gear shifts reduces noise and vibrations. | Automatic transmissions may produce audible gear shift sounds, which some drivers may find engaging or desirable. |
| 4 | Considered well-suited for urban driving and stop-and-go traffic, as the continuous gear ratio adjustment allows for smooth acceleration. | Automatic transmissions can be advantageous for highway driving or towing, providing more responsive power delivery and torque. |
| 5 | CVTs tend to be more affordable to produce, which can result in lower vehicle prices for buyers. | Automatic transmissions may increase the overall cost of the vehicle due to their more complex design and manufacturing process. |
| 6 | Some CVTs have faced durability concerns in the past, although proper maintenance and following manufacturer guidelines can help mitigate potential issues. | Traditional automatic transmissions have a long-standing reputation for reliability, with fewer reported concerns in comparison. |
| 7 | Suitable for a wide range of driving styles, including everyday commuting and long-distance travel. | Preferred by drivers seeking a more engaging and dynamic driving experience, especially in sporty or performance-oriented vehicles. |
| 8 | CVTs provide a seamless and continuous power delivery, eliminating the sensation of gear hunting or abrupt shifts. | Automatic transmissions offer a sense of connection and control through the perceptible gear changes, appealing to some drivers’ preferences. |
| 9 | Fuel efficiency benefits of CVTs can result in long-term savings for buyers who prioritize lower fuel consumption. | Automatic transmissions may have higher fuel consumption but can provide an enjoyable driving experience for those who value traditional gear shifts. |
| 10 | CVTs require specialized knowledge for repairs and maintenance, which can limit the options for DIY enthusiasts. | Routine maintenance and basic repairs for automatic transmissions can be more accessible and manageable for those with general automotive knowledge. |
| 11 | Buyers focused on efficiency and a smooth driving experience may find CVTs aligning with their preferences and priorities. | Enthusiasts seeking a more traditional driving feel or those who prioritize performance may lean towards vehicles with automatic transmissions. |
| 12 | The availability of CVTs in compact and mid-size vehicles often provides buyers with affordable options in these segments. | Automatic transmissions are commonly found across a wide range of vehicle types, providing buyers with ample choices in terms of performance, capability, and brand preference. |
Frequently asked Questions on CVT vs Automatic transmission:
1. Is CVT the same as automatic?
CVT is a type of automatic transmission, but not all automatic transmissions are CVTs. Traditional automatics use fixed gears, while CVTs employ a pulley and belt system to provide infinite gear ratios, optimizing engine performance.
.
2. Is CVT better than automatic?
CVT and automatic transmissions have their own strengths and considerations. CVT excels in fuel efficiency and seamless acceleration, while automatic offers a more engaging driving experience. The choice depends on individual preferences and priorities.
.
3. What are the advantages of CVT over automatic transmission?
CVT offers smoother acceleration, improved fuel efficiency, and a more continuous power delivery. It eliminates gear shifts, reducing power interruptions and enhancing driving comfort. CVTs are also lighter, potentially improving fuel economy.
.
4. Why is CVT cheaper than automatic?
CVTs are more cost-effective to produce due to their simpler mechanical design and fewer moving parts compared to traditional automatics. This can result in lower vehicle prices, especially in compact and mid-size segments.
.
Conclusion
In the realm of transmissions, the choice between CVT and automatic transmission ultimately comes down to personal preferences, driving needs, and priorities. While CVTs excel in fuel efficiency, smoothness, and continuous power delivery, automatic transmissions offer a more engaging driving experience with distinct gear shifts.
It is crucial for car buyers to consider factors such as fuel efficiency, driving comfort, and personal preferences when selecting the transmission that aligns best with their needs.
Ultimately, by understanding the distinctions between CVT and automatic transmissions, drivers can make informed decisions, ensuring an enjoyable and satisfying driving experience tailored to their unique requirements.


![Types of Car Sensors: Functions, Working, Location [with PDF]](https://mechanicalpost.site/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/Different-types-of-Car-Sensors.png)
