What is CNC Machining? A Complete Guide to CNC with PDF
How do incredibly precise metal parts find their way into complex machines like aircraft engines, medical devices, and industrial equipment? The hidden hero behind the scene is CNC machining technology.

This computer-controlled manufacturing process enables cutting metal with unparalleled speed, precision, and repeatability far beyond manual machining alone. From a high-level overview to machining operations, equipment, materials, tolerances, and costs, this guide will reveal everything you need to know about the present and future of CNC manufacturing.
What is CNC machining?
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that uses pre-programmed computer software to control the movement and operation of machine tools and cutting tools to shape stock material into custom-designed parts and products.
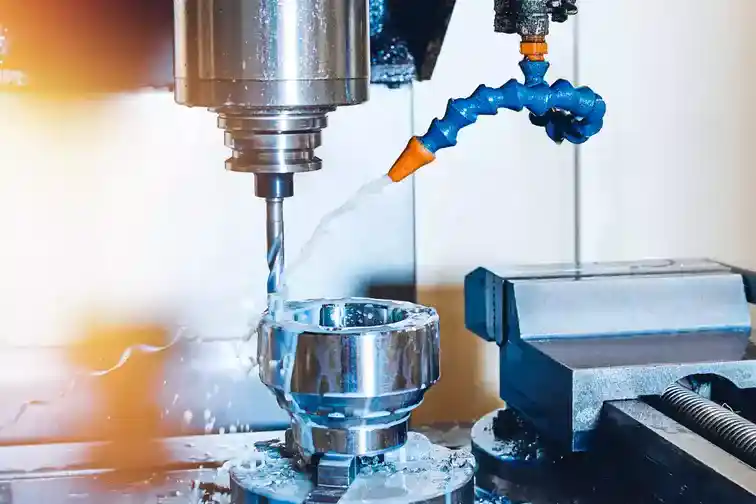

CNC machining is commonly used to produce parts and prototypes across many industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical, electronics, and more. The CNC machining process offers high precision, repeatability, and accuracy as well as increased production efficiency compared to manual machining processes.
How Does CNC Machining Work?
CNC machining works by converting CAD models into CNC code that controls all aspects of the machining process. Here are the basic steps:
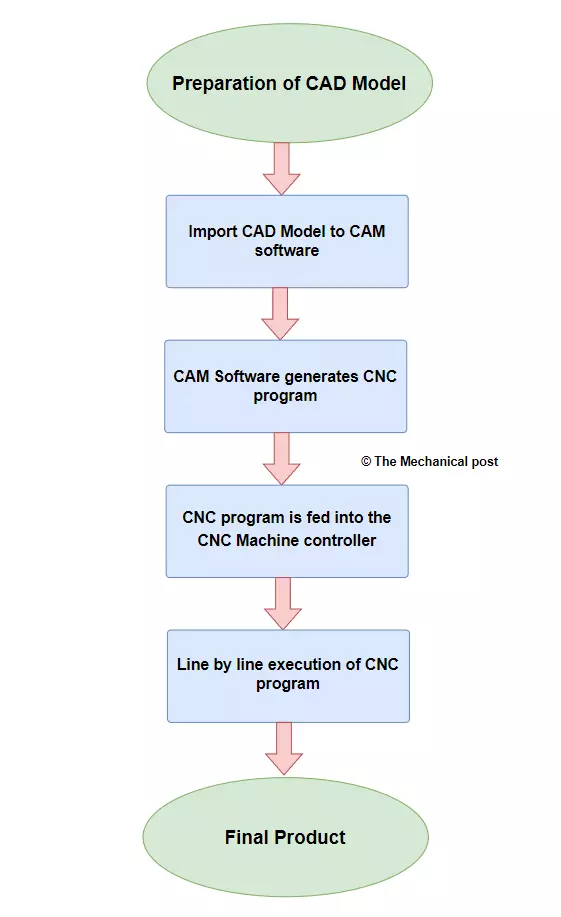
- A CAD model of the desired part is created or imported into CAM software.
- The CAM software converts the CAD model into CNC code (G-code and M-code).
- The CNC G-code and M-code is input into the CNC machine controller which reads it line-by-line.
- As each line of code is read, the CNC machine’s stepper motors position the part and cutting tools according to the coordinates and commands specified in the program.
- The cutting tools are then activated to cut away material to produce the desired part features and geometry.
- The process is repeated automatically until the program is completed and the final part is produced.
CNC machining utilizes computer numerical control to automate and control the machine tools. This eliminates the need for manual operation of levers, wheels and handles which allows for increased precision, speed, and complexity in part production.
Benefits of CNC Machining

There are many benefits that CNC machining offers over manual machining processes:
- Increased speed and efficiency – CNC machines work continuously with minimal human intervention, allowing faster production times. Parts can be produced 24/7.
- Improved accuracy and precision – The programmed commands control the cutting tools to tight tolerances of 0.001″ or 0.002″. Complex 3D contours are easily achieved with advanced CNC machines like the 5-axis CNC machine.
- Excellent repeatability – CNC machines produce identical parts time after time. Once the program is verified, no prototype is required.
- Reduced waste – CNC machining is optimized to minimize raw material waste.
- Flexibility – The same CNC machine can be programmed to produce various parts. Design changes can be accommodated by editing the CNC program.
- Safer working conditions – CNC machines minimize the need for operators to handle dangerous cutting tools.
- Ability to machine hard materials – CNC machines can work with hard metals beyond the capability of manual machining.
Overall, CNC machining improves manufacturing productivity, part accuracy and operating costs compared to relying solely on manual machining processes.
Types of CNC Machines
There are several common types of CNC machines used for machining parts and prototypes:
1. CNC Milling
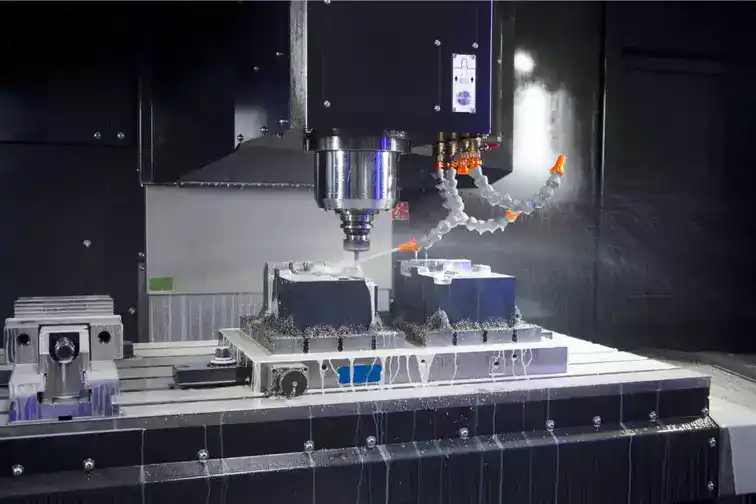

CNC milling machines use rotary cutters to remove material from a stock piece to produce a finished part. The most common CNC milling machines are:
- Vertical machining centers (VMCs) – Mill complex 3D features into parts with a vertically-oriented spindle.
- Horizontal machining centers (HMCs) – Similar to VMCs but with spindle in horizontal orientation. Ideal for high-volume production.
- Gantry routers – Larger machines with gantry frame for milling big parts like wood signs or furniture.
2. CNC Lathes
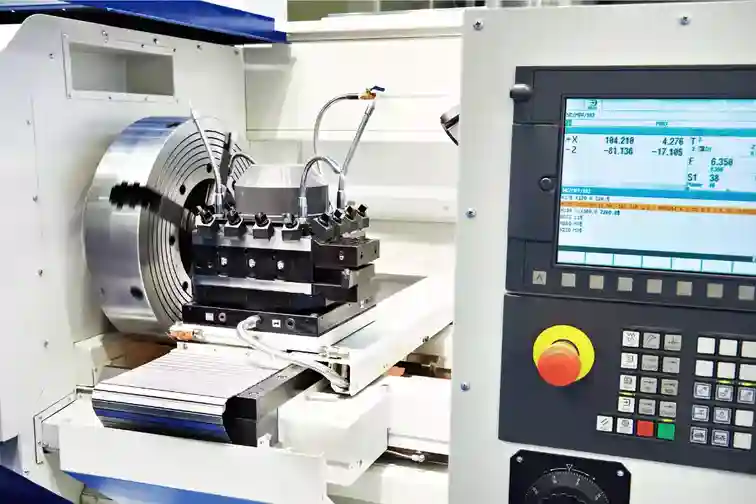

CNC lathes spin the part while a stationary cutting tool machines the material. Used to produce cylindrical parts like bolts, screws, rods and shafts. Unlike traditional lathe machines, CNC lathes are quite superior in quality and machining time.
- 2-axis turning centers – Basic CNC lathes with X/Z axis for machining external diameters.
- Multi-axis turning centers – Allow complex internal features with added Y-axis and milling capability.
- Swiss-style lathes – Use sliding headstock to machine bar stock in one setup.
- Chuckers – Production lathes for high-volume machining small, cylindrical parts.
3. CNC Grinders
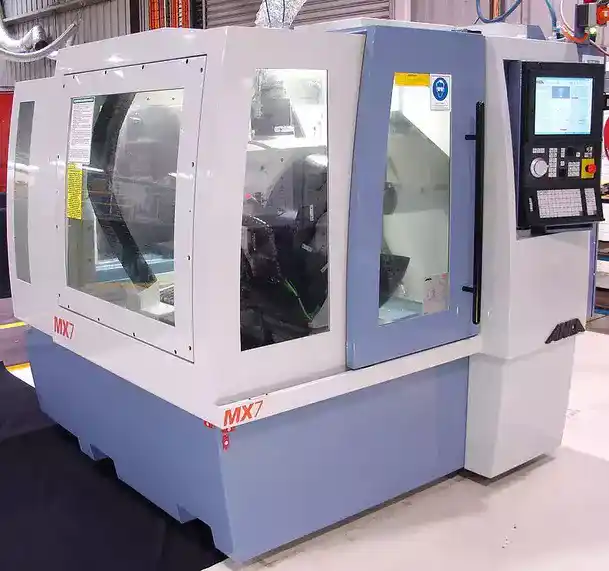

Source: Prbocchi, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
CNC grinders use abrasive wheel cutting to shape parts and cut away excess material. Includes:
- Cylindrical grinders – For external cylindrical surface finishing.
- Creep feed grinders – Remove large amounts of material in rough grinding ops.
- CNC tool & cutter grinders – Sharpen cutting tools to tight tolerances.
- Surface grinders – For flat surface finishing.
- Centerless grinders – Specialized for high-production cylindrical parts.
- ID grinders – Bore grinding internal surfaces to spec.
4. CNC Routers
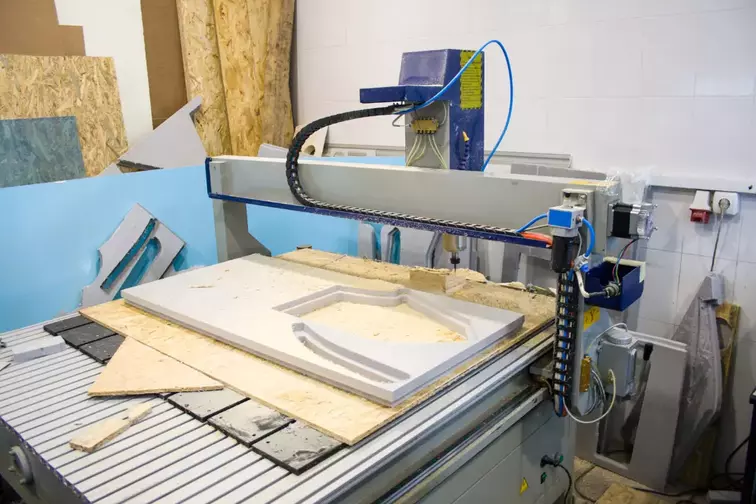

CNC routers utilize rotating cutting tools to cut and shape softer materials like wood, plastics, foam, composites, and light metals. The cutting head moves in 3 axes (X, Y, Z) or more advanced 5-axis routing for angled cuts.
Must Read: How to Machine glass using any CNC Router?
Common in sign-making, woodworking, and prototyping applications. Ideal for accurately cutting 2D profiles from sheet materials. Routers with abrasive waterjet capabilities can cut steel plate. Router work areas range from a few square feet up to 10 x 20 ft or larger.
5. Electrical Discharge Machining

Electric Discharge Machining is a specialized machining process use electrical sparks to erode conductive materials. Ideal for small, complex, hard-to-machine geometries. Includes:
- Wire EDM – Uses thinwire to cut through material.
- Sinker EDM – Shapes parts by submerging in dielectric fluid.
- Hole drill EDM – Bores small, deep holes.
What Can Be Made with CNC Machining?
CNC machining is used to manufacture metal and plastic parts across virtually every industry. Here are some examples of components made through CNC machining processes:
- Automotive – Engine blocks, pistons, valves, gears, axles, brake components
- Aerospace – Turbine blades, landing gear, missile cones, engine parts
- Medical – Dental implants, prosthetics, surgical instruments, medical devices
- Oil & gas – Pump parts, drill bits, hydraulic components, valves
- Electronics – Heat sinks, enclosures, connectors, semiconductors, PCBs
- Industrial machinery – Gears, shafts, bearings, couplings, hydraulic pistons
- Consumer products – Watch cases, power tool housings, furniture hardware
- Defense – Guidance systems, aircraft assemblies, gun components
And many more – virtually any part that can be designed in CAD software can be machined on a CNC machine. The most common materials cut are metals like aluminum, steel, stainless steel, titanium, alloys, and plastics like ABS, PEEK, nylon and acetal.
CNC Machining Tolerance Capabilities
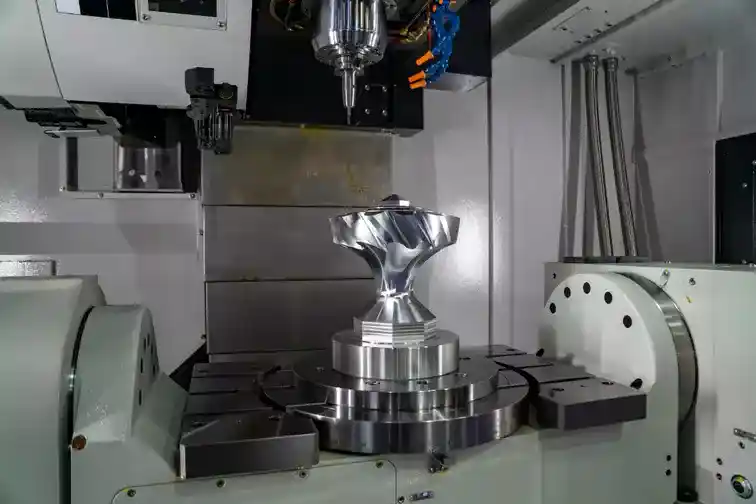

CNC machining can achieve very tight tolerances thanks to the precision inherent in computer numerical control. Here are some examples of tolerances that are possible:
- Dimensions – can routinely hold +/- 0.005” (0.127mm)
- Geometric tolerances – common tolerances include 0.002” cylindricity, 0.0005” runout, 0.001” flatness
- Surface finishes – machined surface finishes can range from 8 Ra up to 63 Ra microinch
Getting the tightest CNC machining tolerances depends on many factors – material being cut, machine rigidity, cutting tools used, coolant, operator skill, environment, program optimization, and more. Working with an experienced CNC machine shop will help determine what tolerances can be realistically held for a given part design and material.
How to Get Started with CNC Machining?
For companies looking to utilize CNC machining, the easiest way to get started is to work with a machine shop offering CNC services. The basic steps are:
- Design the part in CAD software like Solidworks, Autodesk Inventor, or similar.
- Send the CAD file to the CNC machine shop and specify material choice and any critical tolerances.
- The machine shop will program the CAD model and choose optimal tools, speeds and feeds.
- A first-run part is machined, inspected, and sent to the customer for approval.
- Once approved, the machine shop programs the job for production and machines the required quantity of parts.
Reputable machine shops will work closely with customers through the prototyping and production process to ensure the machined parts meet all specifications. They will also provide design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis to help optimize the part design for CNC machining.
Here is the list of the Top 10 Best CNC Machine brands and manufacturers to help you get started
CNC Machining Cost Factors

What determines the cost to CNC machine a part? Here are some of the key variables:
- Part size – Larger or bulkier parts take longer cycle times and require bigger machines.
- Material – Exotic alloys like titanium and Inconel are more expensive than aluminum and steel.
- Tolerances – Tighter tolerances require slower feeds/speeds and more programming.
- Surface finishes – Smoother surface finishes require additional operations.
- Part complexity – Complex designs need more programming and machine setup.
- Quantity – Per-part costs decrease with higher order quantities.
- Secondary operations – Additional ops like tapping holes, deburring, polishing, anodizing etc add to total cost.
- Machine shop overhead – Experience, expertise, and capabilities of the CNC shop influence pricing.
Getting quotes from different machine shops is the best way to determine competitive pricing for a CNC job. Be sure to get DFM feedback to optimize the design for manufacturability and minimize overall costs.
CNC Machining Advantages Over 3D Printing
While additive manufacturing like 3D printing has received much attention for prototype parts, CNC machining offers advantages that make it better suited for many production applications:
Speed – CNC machines can rapidly machine parts in minutes or hours vs. 3D printing which takes many hours to grow a part one layer at a time. For production volumes, CNC is much faster.
Accuracy – CNC machining achieves much tighter tolerances and better dimensional accuracy compared to most 3D printing processes.
Materials – CNC machines cut hard engineering materials like metals and high-performance plastics which cannot be 3D printed cost effectively.
Surface finish – The fine surface finishes and lack of layer lines achievable with CNC machining are superior to basic 3D printing. No additional finishing is required with CNC parts in most cases.
Production quantities – CNC machining is ideal for medium to high production volumes from dozens to thousands of parts as it has high repeatability. 3D printing comes with size limitations and long production times.
Cost – For serious production runs, CNC machining is lower cost as machine time is faster and material waste is minimized. No expensive binders or bulk powder/filament.
For companies looking to manufacture production parts and components, CNC machining remains the go-to process for quality, speed and lower costs at scale. 3D printing excels at earlier stage prototyping where design flexibility and quick turnaround is most important.

FAQ on CNC Machining
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about CNC machining:
What materials can be machined on a CNC?
CNC machines can process a wide variety of materials including metals like aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass, titanium, inconel, and plastics such as ABS, PEEK, nylon, acetal, PTFE, and polycarbonate. Almost any material that is rigid enough to withstand the machining forces can be CNC machined.
.
What is the difference between CNC milling and CNC turning?
CNC milling uses rotating cutting tools to remove material and make complex shapes. CNC turning spins the part while a cutter machines the outside diameter and faces. Milling creates 3D features while turning machines round, cylindrical forms.
.
What tolerances can CNC machining achieve?
Typical CNC machining can hold dimensional tolerances of +/- 0.005” and geometric tolerance of 0.001” to 0.002”. However, skilled CNC machinists can achieve even tighter tolerances down to +/- 0.001” for precision applications.
.
How much does CNC machining cost?
CNC machining costs depend on many factors but typical per part costs may range from $1 to $500. High volume production jobs allow the per part cost to decrease significantly. Getting quotes from CNC machine shops is recommended.
.
How fast is CNC machining?
Simple parts can be machined in under a minute. More complex parts may take 15 minutes to a few hours depending on the operations required. CNC machining is much faster than manual machining or 3D printing for production quantities.
.
Is CNC machining good for prototypes?
Yes, CNC machining can produce high quality functional prototypes quickly out of production-intent materials. Changes can be made by just editing the CNC program making it ideal for prototyping iterations.
.
Is there CNC machining software I can buy?
Yes, there are complete CAM software packages like Mastercam, SolidCAM, and Fusion 360 which allow you to program and simulate CNC machining operations right on your desktop. These range from a few thousand dollars to over ten thousand for a full license.
.
Conclusion on CNC Machining
CNC machining is an efficient, accurate and repeatable manufacturing process ideal for taking a CAD design all the way through to finished production parts. The benefits of CNC machining include:
- Faster production with high automation
- Superior accuracy and repeatability
- Excellent for medium to high production runs
- Ability to machine hard, engineering-grade materials
- Wide material selection – metals, plastics, composites
- Complex 3D part geometries achievable
- Smoother surface finishes than 3D printing
- Proven, cost-effective process for manufacturing
This guide covered the key aspects of what CNC machining is, how it works, the types of CNC machines, as well as the many benefits this versatile manufacturing process provides to a wide range of industries.
I hope this detailed guide helps explain the core aspects of CNC machining and the powerful benefits this technology offers manufacturers. Let me know if you have any other questions!



![What is Industrial Automation and its Types? [with PDF]](https://mechanicalpost.site/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/What-is-Industrial-Automation-ad-its-types.webp)

Enjoyed reading the article above, really explains everything in detail,the article is very interesting and effective